Confounding and Blocking in 2k Factorial Designs. 82 Calculation of Aliases.

5 4 7 1 Full Factorial Example
For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs.
. In order to select a 18 fraction of the full factorial we will need to choose 3 generators and make sure. Amount of catalyst charge 1 temperature 2 pressure 3 and concentration of one of the reactants 4. Neffect24 divided by df1 and turned into an F-ratio.
There are very useful summaries of two-level fractional factorial designs for up to 11 factors originally published in the book Statistics for Experimenters by GEP. 7 Two Level Fractional Factorial Designs. How to build.
So for example a 43 factorial design would involve two independent variables with four levels for one IV and three levels for the other IV. The Advantages and Challenges of Using Factorial Designs. 18th fractional factorial of a 26 design.
We refer to the three levels of the factors as low 0 intermediate 1 and high 2. High and watering frequency daily vs. This design is called a 25 1 fractional factorial design.
For example runs 2 and 4 represent factor A at the high level. The 3k Factorial Design is a factorial arrangement with k factors each at three levels. In general a 2k-p design is a frac12p fraction of a 2k design using 2k-p runs.
10112 Example - 24 design for studying a chemical reaction. The average response from these runs can be contrasted with those from runs 1. Rather than the 32 runs that would be required for the full 2 5 factorial experiment this experiment requires only eight runs.
This is an example of a 22 factorial design because there are two independent variables each with two levels. 81 Calculation of Effects. Misuse of the ANOVA for 2k.
The three inputs factors that are considered important to the operation are Speed X 1 Feed X 2 and Depth X 3. Start with full factorial design and then introduce new factors by identifying with interaction effects of the old. A design with p such generators is a 1l pl p fraction of the full factorial design.
The following is an example of a full factorial design with 3 factors that also illustrates replication randomization and added center points. 61 - The Simplest Case. Full factorial is 2k Fractional Factorial is 2kp Degree of fraction is 2p 25-5 Half-Fraction 2k Factorials This is one half the usual number of runs Similar to blocking procedure Choose a generator which divides efiects into two Based on pluses and minuses of one factor Deflning Relation.
These numbers are also shown in Figure 31. This design is called a quarter fraction of the full 25 or a 25-2 design a two to the five minus two design. If equal sample sizes are taken for each of the possible factor combinations then the design is a balanced two-factor factorial design.
4 FACTORIAL DESIGNS 41 Two Factor Factorial Designs A two-factor factorial design is an experimental design in which data is collected for all possible combinations of the levels of the two factors of interest. Rule for writing a 2 k full factorial in standard order We can readily generalize the 2 3 standard order matrix to a. Weekly on the growth of a certain species of plant.
Thus we want to run a 12 fraction of a 25 design. 63 - Unreplicated 2k Factorial Designs. A 23-1 design 24-1 design 25-2 design etc 2n-m.
Hunter New York John Wiley Sons 1978 and also given in the book Design and Analysis of Experiments 5th edition. The 2k Factorial Design. For example a 2 5 2 design is 14 of a two level five factor factorial design.
5 Blocking in 2 k Designs. Fractional factorial designs A design with factors at two levels. 52 - Another Factorial Design Example - Cloth Dyes.
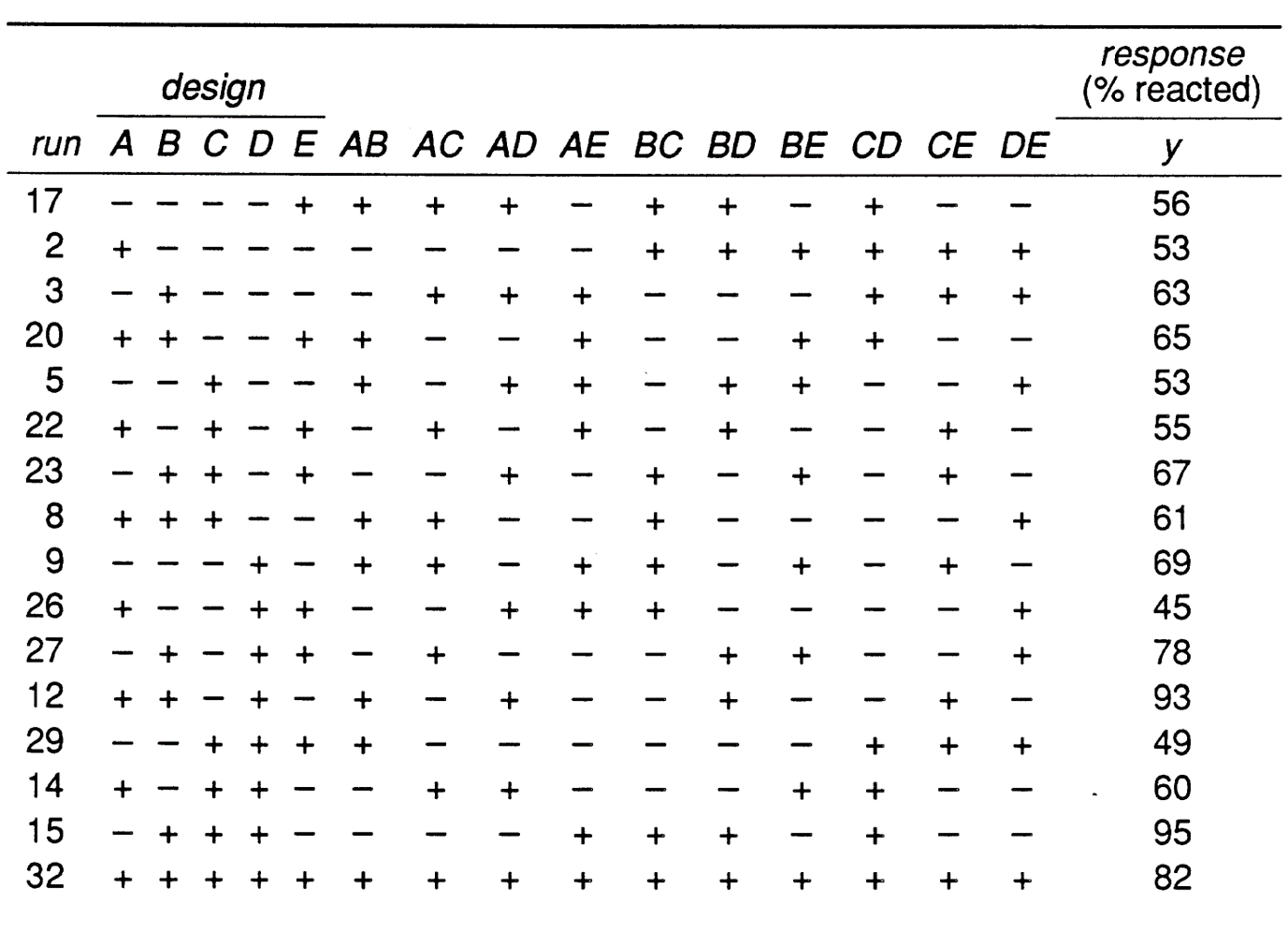
A process development experiment studied four factors in a 24 factorial design. A full factorial for the five factors A B C D E would have needed 25 32 runs. 62 - Estimated Effects and the Sum of Squares from the Contrasts.
This design is called a 2 1 fractional factorial design. Partitioned into individual SS for effects each equal to. 2 Level Factorial Design with Four Blocks.
52 Unreplicated 2 k Designs in 2 p Blocks. Standard Order for a 2 k Level Factorial Design. We consider this type of design through two examples.
First we will look at an example with 6 factors and we select a 26-3 design or a 18th fractional factorial of a 26 design. The response y is the percent conversion at each of the 16 run conditions. Useful fractional factorial designs for up to 10 factors are summarized here.
For example in a 32 design the nine treatment combinations are denoted by 00 01 10 02 20 11 12 21 22. 3-2 The points for the factorial designs are labeled in a standard order starting with all low levels and ending with all high levels. For example run 1 is made at the low setting of all three factors.
51 - Factorial Designs with Two Treatment Factors. Suppose there are 5 factors of interest A B C D and E and there are only enough resources for 16 experimental runs. One of the big advantages of factorial designs is that they allow researchers to look for interactions between independent variables.
A 12 fraction can be generated from any interaction but using the highest-order interaction is the. The design is. Only 14 were run.
Suppose that we wish to improve the yield of a polishing operation. For 2kdesigns the use of the ANOVA is confusing and makes little sense. Two Level Factorial Design with Two Blocks.

Full Factorial Design For 2 Factors And 2 Levels A Design Matrix Download Scientific Diagram

2 K Factorial Design Tool Real Statistics Using Excel
Two Level Factorial Experiments Reliawiki

Highly Fractional Factorial Designs Reliawiki
Two Level Factorial Experiments Reliawiki

R How To Simulate An Unreplicated Factorial Design Cross Validated
0 comments
Post a Comment